© Special Astrophysical Observatory of the Russian Academy of
Sciences
The
instrument
setup
at
R=100.000
enables
the
observation
of
stars
in
the
11m-12m
range
under
normal
weather
conditions
(with
a
seeing
quality
~1.5”)
using
one-hour
exposures
and
achieving
a
signal-to-noise
ratio
of
100.
The
expected
ultimate
accuracy
for
radial
velocity
measurements
of
cool
stars
is
1
m/s
or
better,
while
the
precision
for
magnetic
field
measurements
of
cool
stars
is
anticipated
to
be
1
G
or
better.
In
its
final
configuration,
the
spectrograph
will
be
equipped
with
an
interferometric
control
system
utilizing
a
vacuum-stabilized
Fabry-Perot
interferometer
to
achieve
exceptionally
high
wavelength calibration precision of 50 cm/sec.
The Spectrograph Design
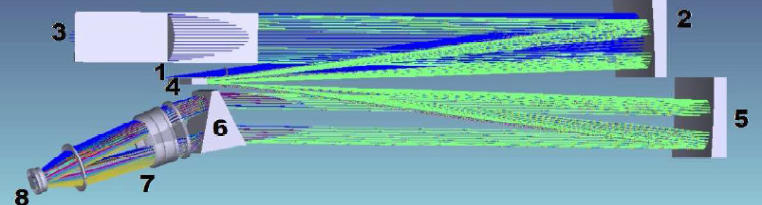
The design of the spectrograph is founded on the traditional optical configuration referred to as the "white pupil" (Dekker et al. 2000). Unlike conventional spectrograph designs, the "white pupil" offers several significant benefits. Key advantages include a reduction in the entrance aperture of the projection camera and minimized stray light. The optical arrangement of the spectrograph is illustrated above (for further details, see Valyavin et al. 2014) and comprises the following components: • Slit assembly 1 fed with five fiber terminations • Off-axis main collimator 2 and transfer collimator 5 with parabolic- shaped surfaces • Mosaic of two echelle gratings 3 • Flat mirror 4 • Cross disperser 6 -- a combination of a prism and a grating • CCD detector 8 • Focusing camera 7Parameters
• Collimator -- focal distance 2175 mm, diameter 187 mm • Echelle gratings’ blaze angle -- 75.5° (R4). • Cross disperser prism’s glass -- PBM2Y Ohara • Cross disperser grating -- 200 groovs/mm operating in the first order. The refraction angle -- 40° • CCD detector -- 4k x 4k chip with a pixel size of 15 μm (http://www.e2v.com) • Focusing camera -- a F/2.35 lens combination consisting of six spherical optical elements with an effective focal length of 470 mm.References
Dekker et al. 2000 // Dekker, H., D’Odorico, S., Kaufer, A., Delabre, B., & Kotzlowski, H. 2000, Proc. SPIE 4008, 534 Valyavin et al. 2014 // Valyavin, G. G., Bychkov, V. D., Yushkin, M. V., Galazutdinov, G. A., Drabek, S. V., Shergin, V. S., Sarkisyan, A. N., Semenko, E. A., Perkov, A. V., Sazonenko, D. A., Kukushkin, D. E., Bakholdin, A. V., Burlakova, T. E., Kravchenko, V. M., Kudryavtsev, D. O., Pritychenko, A. M., Kryukov, P. G., Semjonov, S. L., Musaev, F. A., & Fabrika, S. N. 2014, Astrophysical Bulletin, 69, 224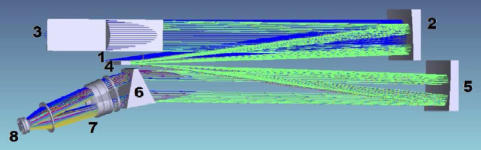


© Special Astrophysical Observatory of the Russian Academy of Sciences
The
instrument
setup
at
R=100.000
enables
the
observation
of
stars
in
the
11m-12m
range
under
normal
weather
conditions
(with
a
seeing
quality
~1.5”)
using
one-hour
exposures
and
achieving
a
signal-to-noise
ratio
of
100.
The
expected
ultimate
accuracy
for
radial
velocity
measurements
of
cool
stars
is
1
m/s
or
better,
while
the
precision
for
magnetic
field
measurements
of
cool
stars
is
anticipated
to
be
1
G
or
better.
In
its
final
configuration,
the
spectrograph
will
be
equipped
with
an
interferometric
control
system
utilizing
a
vacuum-stabilized
Fabry-Perot
interferometer
to
achieve exceptionally high wavelength calibration precision of 50 cm/sec.
The Spectrograph Design
The design of the spectrograph is founded on the traditional optical configuration referred to as the "white pupil" (Dekker et al. 2000). Unlike conventional spectrograph designs, the "white pupil" offers several significant benefits. Key advantages include a reduction in the entrance aperture of the projection camera and minimized stray light. The optical arrangement of the spectrograph is illustrated above (for further details, see Valyavin et al. 2014) and comprises the following components: • Slit assembly 1 fed with five fiber terminations • Off-axis main collimator 2 and transfer collimator 5 with parabolic- shaped surfaces • Mosaic of two echelle gratings 3 • Flat mirror 4 • Cross disperser 6 -- a combination of a prism and a grating • CCD detector 8 • Focusing camera 7Parameters
• Collimator -- focal distance 2175 mm, diameter 187 mm • Echelle gratings’ blaze angle -- 75.5° (R4). • Cross disperser prism’s glass -- PBM2Y Ohara • Cross disperser grating -- 200 groovs/mm operating in the first order. The refraction angle -- 40° • CCD detector -- 4k x 4k chip with a pixel size of 15 μm (http://www.e2v.com) • Focusing camera -- a F/2.35 lens combination consisting of six spherical optical elements with an effective focal length of 470 mm.References
Dekker et al. 2000 // Dekker, H., D’Odorico, S., Kaufer, A., Delabre, B., & Kotzlowski, H. 2000, Proc. SPIE 4008, 534 Valyavin et al. 2014 // Valyavin, G. G., Bychkov, V. D., Yushkin, M. V., Galazutdinov, G. A., Drabek, S. V., Shergin, V. S., Sarkisyan, A. N., Semenko, E. A., Perkov, A. V., Sazonenko, D. A., Kukushkin, D. E., Bakholdin, A. V., Burlakova, T. E., Kravchenko, V. M., Kudryavtsev, D. O., Pritychenko, A. M., Kryukov, P. G., Semjonov, S. L., Musaev, F. A., & Fabrika, S. N. 2014, Astrophysical Bulletin, 69, 224